A checker plate, also known as a tread plate or diamond plate, is a type of metal sheet with a raised pattern on its surface. This distinctive texture enhances grip, making it a popular solution for non-slip flooring and industrial applications. Checker plates are typically made from steel, aluminum, or stainless steel, and are widely used across construction, transportation, and manufacturing industries.
1. Definition and Key Features of Checker Plates
Checker plates are flat metal sheets embossed with regular patterns such as diamonds, teardrops, or lines. These raised textures provide both aesthetic appeal and functional anti-slip properties. The most common metals used include:
Steel checker plate: Strong and durable, ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Aluminum tread plate: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, commonly used in transport and decorative uses.
Stainless steel checker plate: Offers high resistance to corrosion and is suitable for wet or hygienic environments.
The raised surface helps prevent slipping, especially in wet, oily, or industrial settings. The pattern also adds strength without significantly increasing weight.
2. Common Types of Checker Plates and Their Materials
Checker plates are available in various patterns and materials depending on the intended use:
Diamond plate: The most iconic style, with raised diamond-shaped ridges.

5-bar checker plate: Common in flooring applications, with five parallel bars forming a slip-resistant pattern.
Teardrop tread plate: Features rounded, droplet-shaped patterns.
Flat back vs. full pattern: Some plates have a flat back for easier installation on flat surfaces.
Materials:
Steel checker plate is known for its load-bearing capacity.
Aluminum checker plate is preferred in automotive and marine applications.
Stainless steel checker plate excels in food processing areas or corrosive environments.
3. Main Applications of Checker Plates in Industrial and Commercial Use
Checker plates are versatile and can be found in a wide range of industries. Common applications include:
Industrial flooring: Factory floors, warehouse platforms, and mezzanine surfaces.
Stair treads and walkways: Offers safe footing in high-traffic or elevated areas.
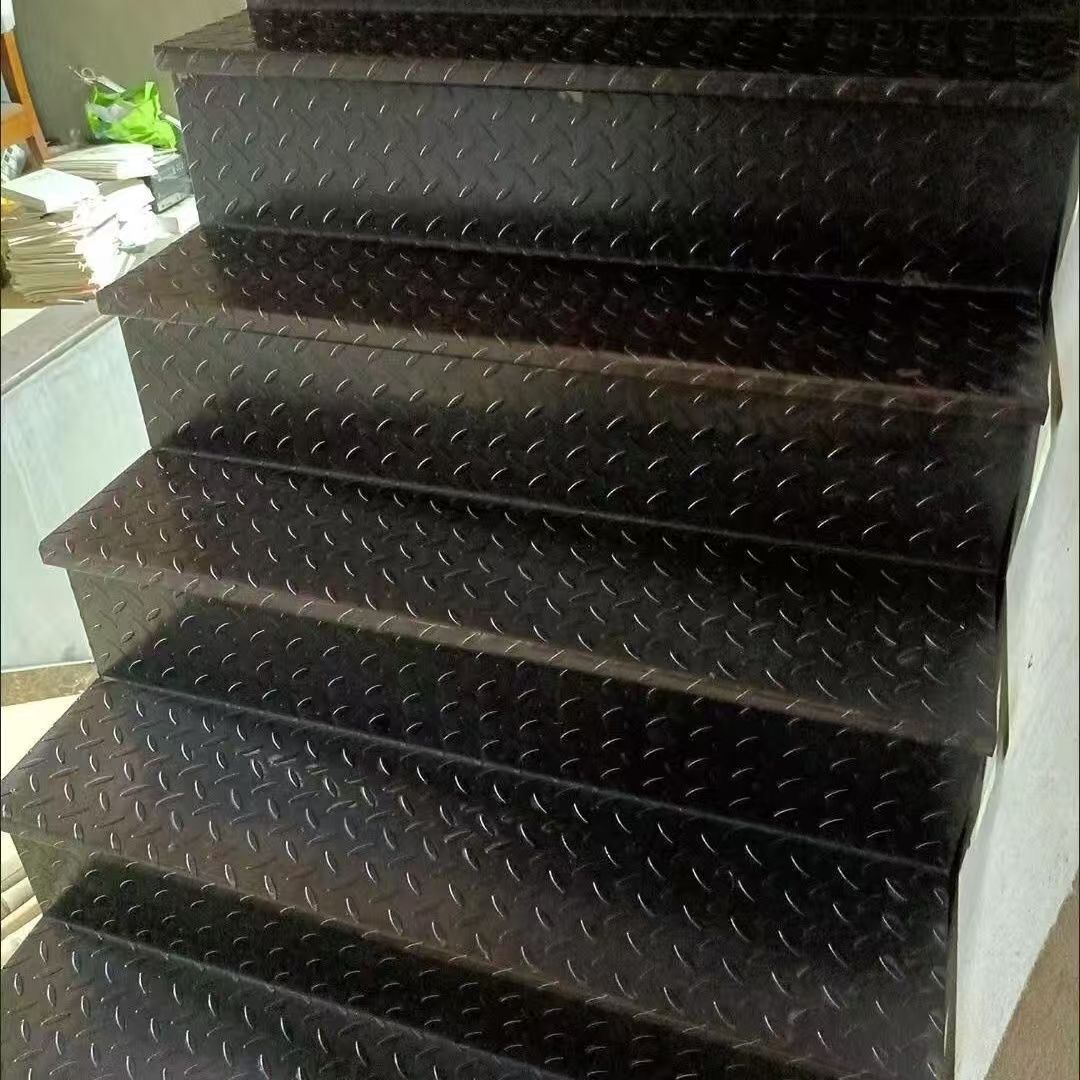

Vehicle flooring: Used in trucks, trailers, emergency vehicles, and fire engines.
Ramps and loading docks: Helps prevent slipping during cargo transfer.
Decorative uses: Retail displays, toolboxes, walls, and furniture.
Because metal checker plates combine durability with slip resistance, they are ideal for environments that prioritize both safety and long service life.
4. Advantages of Using Checker Plates for Safety and Durability
Checker plates offer several advantages:
Slip resistance: Raised patterns reduce the risk of accidents caused by slippery surfaces.
High strength-to-weight ratio: Especially in aluminum tread plates, the design adds rigidity without extra bulk.
Corrosion resistance: Stainless and aluminum versions are rust-resistant.

Easy to fabricate: Can be cut, welded, and installed using common metalworking tools.
Aesthetic appeal: The patterned look adds a professional touch to functional surfaces.
Choosing the right steel checker plate or metal checker plate ensures long-term performance with minimal maintenance.
5. How to Choose the Right Checker Plate for Your Project
When selecting a checker plate, consider these factors:
Load requirements: Steel checker plates are best for heavy machinery and industrial flooring.
Environmental conditions: Use aluminum or stainless steel in wet, corrosive, or outdoor settings.
Thickness: Thicker plates offer more strength but are heavier and costlier.
Pattern type: Choose the pattern that offers the best grip for your use case.
Finish: Polished finishes for aesthetics; mill finish for utility-focused applications.
Consult with your supplier to ensure the checker plate matches your project’s mechanical and environmental demands.