Grating products are essential structural materials in modern construction, infrastructure, and urban management. Widely used in drainage systems, surface pavements, ventilation systems, and other fields, they ensure the stability, durability, and functionality of various structures. As the demands for high-performance building materials increase, the choice of grating material becomes more critical. Factors such as load-bearing capacity, corrosion resistance, cost, and environmental compatibility must be carefully considered when selecting the most appropriate material. This article explores four common types of grating materials—steel, aluminum alloy, stainless steel, and plastic—highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses, helping engineers and designers make informed decisions.
1. Galvanized steel grating: High Load-Bearing Capacity and Durability
Galvanized steel grating is one of the most commonly used materials, particularly in heavy-duty applications like roadways, bridges, industrial facilities, and parking lots. Its primary advantage is its high load-bearing capacity and stability, making it ideal for applications that require structural strength.
Advantages: Galvanized steel grating is widely regarded for its strength, capable of handling substantial mechanical loads. It is often used in heavy-duty industrial environments, such as areas with significant vehicle or equipment traffic. Moreover, galvanized steel grating is typically treated with hot-dip galvanization, which enhances its corrosion resistance and extends its lifespan, particularly in moderate environments.
Application Scenarios: Galvanized steel grating is ideal for use in environments such as factories, parking lots, warehouses, and other areas where the structure needs to endure heavy loads and constant wear and tear.
Disadvantages: The main drawback of galvanized steel grating is its weight. It is heavier than other materials, which can increase installation costs and labor. Additionally, although galvanized steel resists corrosion to some extent, it may still rust when exposed to extreme weather conditions, especially in coastal or highly humid environments.
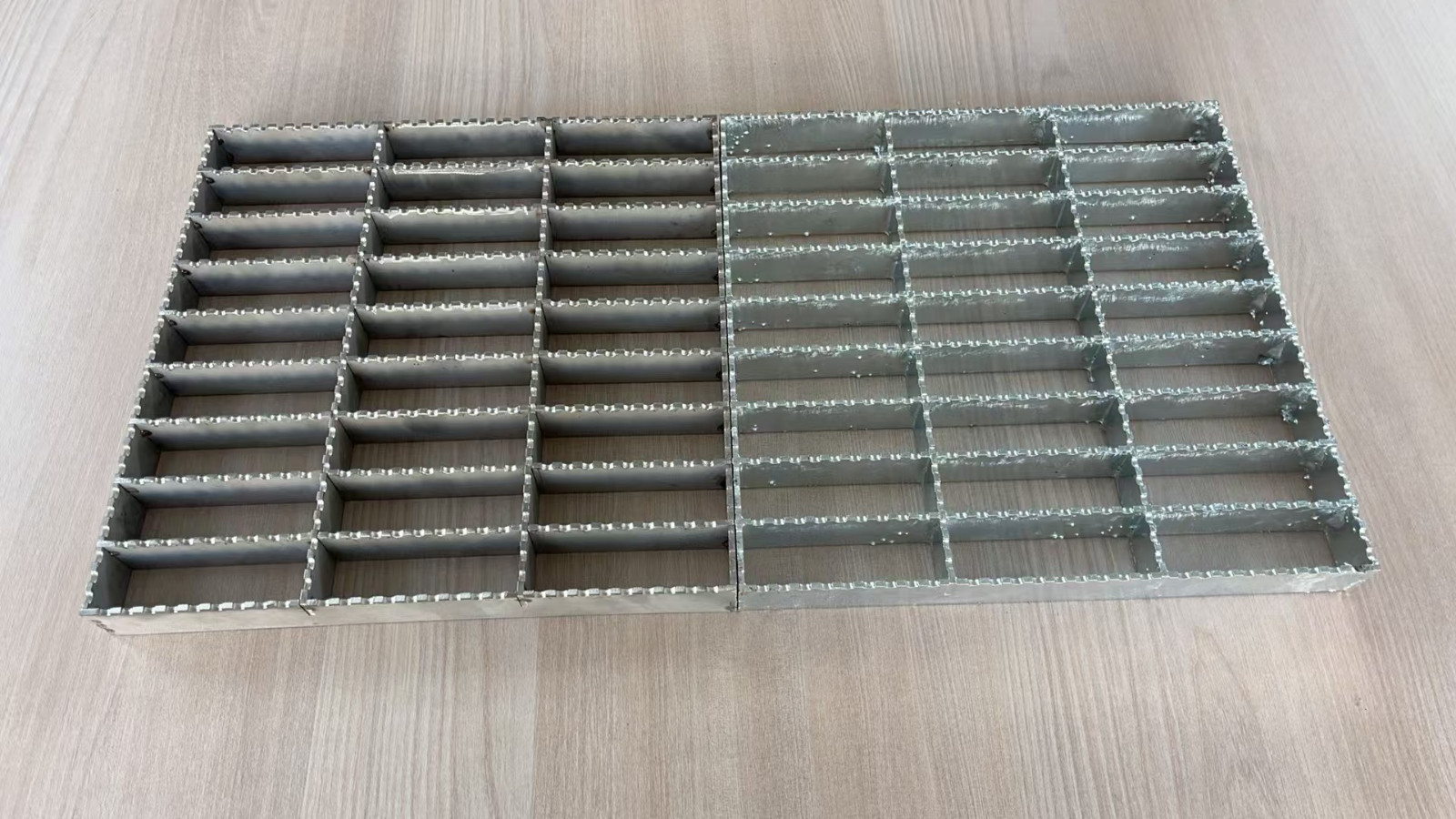

2. Aluminum Alloy Gratings: Lightweight and Aesthetic Appeal
Aluminum alloy grating offers a lighter, more corrosion-resistant alternative to steel, often chosen for applications where both aesthetic appeal and lightweight design are priorities. It combines strength with exceptional corrosion resistance, making it suitable for environments exposed to moisture or chemicals.
Advantages: The primary advantage of aluminum alloy grating is its lightweight nature, making it easier to handle and install. It is also highly resistant to corrosion, particularly in moist or coastal environments. Furthermore, aluminum grating can be customized with various finishes, such as anodizing or painting, giving it a sleek and modern appearance. This aesthetic versatility makes it a preferred choice for projects with design considerations.
Application Scenarios: Aluminum grating is often used in commercial buildings, outdoor walkways, landscaping, and decorative applications. It is ideal for areas that require a balance of corrosion resistance, visual appeal, and lightweight material properties, such as shopping malls, public spaces, and office complexes.
Disadvantages: While aluminum grating is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, its load-bearing capacity is lower than that of steel or stainless steel. It is unsuitable for areas that need to support heavy loads or heavy traffic. Additionally, the cost of aluminum grating is generally higher than that of steel or plastic, which might be a concern for projects with tight budgets.
3. Stainless Steel Gratings: Exceptional Corrosion Resistance and High Temperature Resistance
Stainless steel grating is renowned for its outstanding corrosion resistance, high temperature tolerance, and long-term durability. These characteristics make it the preferred material for harsh environments like chemical plants, offshore platforms, and high-temperature industrial settings.
Advantages: Stainless steel grating is famous for its superior corrosion resistance, particularly in environments exposed to corrosive chemicals, moisture, and salt. Additionally, it is extremely durable and can withstand high mechanical stress. Stainless steel also offers excellent resistance to high temperatures, making it ideal for applications in factories, power plants, and other heat-intensive environments.
Application Scenarios: Stainless steel grating is commonly used in chemical processing plants, marine platforms, power plants, and environments where high corrosion resistance and strength are necessary. It is also widely used in industries that require hygiene and safety standards, such as food processing or pharmaceutical plants.
Disadvantages: The primary disadvantage of stainless steel grating is its high cost. Stainless steel is one of the most expensive grating materials, which can significantly increase the cost of a project. Moreover, while stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, it may still deteriorate under prolonged exposure to extreme acidic or alkaline substances.
4. Plastic Gratings: Cost-Effective and Corrosion-Resistant for Light-Duty Applications
Plastic grating, made from materials like polypropylene or polyethylene, is a highly cost-effective option for light-duty applications where corrosion resistance is required but heavy load-bearing is not a priority. It has become increasingly popular in various industries due to its affordability and practicality.
Advantages: The most notable advantage of plastic grating is its low cost and light weight, making it an economical choice for large-scale installations. Plastic grating is also highly resistant to corrosion and can endure exposure to chemicals and moisture. It is available in various colors and designs, offering flexibility for aesthetic purposes.
Application Scenarios: Plastic grating is often used in drainage systems, walkways, landscaping, and light-duty industrial applications. It is also commonly found in agricultural settings or areas where heavy traffic and high loads are not concerns.
Disadvantages: Plastic grating is not suitable for heavy-duty applications, as it has a low load-bearing capacity compared to steel and stainless steel. Furthermore, plastic grating may become brittle over time, particularly if exposed to UV rays or extreme temperatures, reducing its durability.
5. Comprehensive Comparison: Choosing the Right Material for Specific Needs
Each grating material offers distinct advantages and limitations, so selecting the most suitable material depends on several factors, including load-bearing requirements, environmental conditions, budget, and design preferences.
Load Requirements: For heavy-duty environments, steel or stainless steel grating is the best choice due to their high load-bearing capacities. Aluminum and plastic are better suited for lighter applications.
Environmental Conditions: In environments where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or salt is common, stainless steel and plastic are excellent choices due to their corrosion resistance. Aluminum is also suitable for humid environments, though its strength may not match that of stainless steel.
Cost: Plastic grating is the most affordable material, while stainless steel tends to be the most expensive. Steel and aluminum offer a balance between cost and performance.
Aesthetic Requirements: Aluminum and stainless steel are often preferred for architectural and decorative applications because of their sleek appearance and customizable finishes.
6. Conclusion
Choosing the right grating material is a critical decision in modern construction and infrastructure projects. It is not only a technical consideration but also a matter of balancing performance, durability, cost, and environmental impact. By understanding the characteristics of steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and plastic grating, engineers and architects can make the most appropriate choice for specific applications. Whether it’s steel for heavy-duty projects, aluminum for aesthetic and lightweight designs, stainless steel for harsh environments, or plastic for cost-effective solutions, a careful evaluation of these factors will ensure that the material chosen meets both functional and budgetary requirements.
As urbanization continues to expand and industries evolve, the development and application of grating materials will adapt to meet emerging challenges, driving the future of construction materials and pushing the boundaries of performance and sustainability.